Deep vein thrombosis is a preventable disease caused by changes in blood flow, vessel wall injuries and coagulation disorders. The most important factor in deep vein thrombosis, which can be life-threatening if left untreated, is the disruption of the coagulation system.
Deep vein thrombosis, which is defined as blockage of the deep vein in the leg with a clot, occurs for different reasons. There are reasons such as lying still for a long time, pregnancy, cancer treatment, being over the ideal weight or undergoing brain surgery.
What are the Symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis?
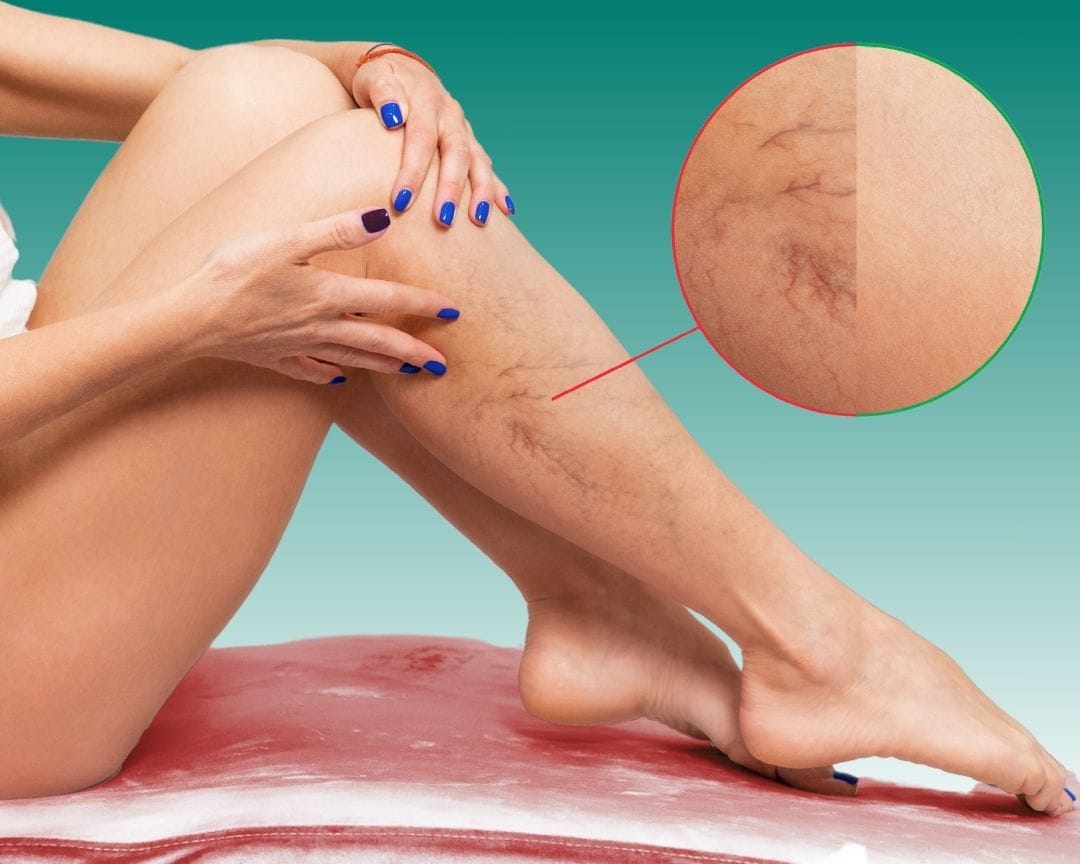
Although it causes high fever in the patient, sudden swelling, redness and pain in the leg that restricts movement are among the most prominent findings. However, the symptoms of pain and swelling vary depending on the location of the problem. Late complications include edema formation and cramps, as well as deformation of the skin structure of the area where the thrombosis is located. If there is a delay in the treatment of deep vein thrombosis, the leg will harden and whiten, the leg will become cold and water vesicles will begin to form. At the same time, ulcers are formed with the deterioration of the circulatory system.
New Methods in the Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis
Pharmacomechanical treatment is currently used in cases of early deep vein thrombosis. This method is the removal of the clot by entering the vein with intravenous clot-busting catheters that have been specially developed in recent years. After this procedure, a catheter that releases clot-dissolving drugs is left in the vein for 24 hours.
In the treatment of deep vein thrombosis diagnosed within the first 48 hours, the clot seen in the deep vein above the knee and in the abdomen is removed by making a small incision in the groin and entering with a special balloon catheter. If the clot is seen in an area below the knee, the clot dissolving drug is systemically delivered to the vein to dissolve the clot.
What are the Wrong Practices in Deep Vein Thrombosis Treatment?
Diagnosis without Doppler test or misdiagnosis, as well as the use of antibiotics or anticoagulant-like blood thinners are the wrong practices in the treatment process. In particular, the use of blood thinners is not effective in eliminating the existing clot. If the correct treatment is delayed, swelling in the patient’s leg and ulcers in the ankles may occur.
Deep Vein Thrombosis Symptoms
The symptoms of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) symptoms could be:
- Leg swelling
- Leg cramps, pain, or soreness that usually start in the calves
- Color changes on the legs like purple or red depending on the hue of your skin
- The sensation of warmth is felt on the leg that is affected
- Deep vein thrombosis may occur without any obvious symptom
Deep Vein Thrombosis Risk factors
Numerous factors can increase the likelihood that you will develop DVT. (DVT). The more risk factors you face the higher your chance of developing DVT. Risk factors for DVT include:
Age: The age of 60 is a factor in increasing the chance of DVT. However, DVT is a possibility at any time.
The lack of movement. If the legs aren’t moving for long periods the calf muscles do not tighten (contract). Muscle contractions aid in blood flow. When you sit for long periods of time like when flying or driving, increases the chance of developing DVT. Also, long-term bed rest that could be the result of a lengthy hospital stay or from a medical condition like paralysis.
Surgery or injury: Injuries to the veins or surgical procedure can increase the chance for blood clots.
Pregnancy: The pressure of pregnancy increases in the veins that run through the legs and pelvis. The risk of blood clots that result from pregnancy may last up to six weeks following the birth of a baby. The people who have an genetic clotting disorder are particularly susceptible.
Birth control tablets (oral contraceptives) or hormone replacement therapy. Both increase blood’s capacity to form clots.
Being overweight or obese. Being overweight causes pressure on the veins in the pelvis and legs.
Smoking: Smoking influences the way blood flows and clots. This could increase the chance of DVT.
Cancer: Certain cancers cause an increase in the amount of blood-borne substances which causes blood to form clots. Certain cancer treatments can also increase the risk that blood clots will form.
Heart failure: Heart failure is a risk factor for the development of DVT and embolisms in the pulmonary tract. Because the lungs and the heart do not function properly in patients with heart disease The symptoms triggered by even a minor pulmonary embolism can be more obvious.
Inflammatory intestinal disease. Crohn’s disease or ulcerative Colitis can increase the chance of DVT.
A family or personal background of DVT or an embolism in the pulmonary tract (PE). If you or anyone in your family has been diagnosed with either or both of these diseases, you could be more at risk of developing DVT.
Genetics: Some people suffer from DNA changes which cause blood to clot quicker. One example is factor V Leiden. The inherited disorder alters one of the factors that cause clots in blood. A genetically inherited condition by itself may cause blood clots, unless coupled by other factors that increase the risk of developing.
Sometimes an enlargement of blood in a vein may be detected without a risk reason. This is known as an unprovoked venous blood thromboembolism (VTE).
Can a patient who arrives late be saved?
First of all, the patient is evaluated with a very good physical examination and a detailed doppler test. In the late period, successful results can be achieved with clot dissolving medication. The total health status of the patient and the condition of the vein in which the clot is seen are evaluated and the patient is hospitalized and both the ligation of the responsible veins and the wounds formed are healed quickly.
What should be done after deep vein thrombosis treatment?
Patients suffering from deep vein thrombosis should definitely be evaluated for INR after the first attack and blood thinners should be used. Thus, a new clot formation is prevented.
Nowadays, neovoral anticoagulant drugs (NACs) can be administered without a continuous blood test, providing comfort to the patient.
What happens if deep vein thrombosis is not treated?
The swelling in the leg may become permanent and scars may open. It can also cause death by throwing a clot into the lung. If a patient with deep vein thrombosis has swelling in the leg, difficulty in breathing and pain in the chest, the possibility of a clot in the lung should be evaluated.
What to avoid with deep vein thrombosis?
Don’t stand or sit in one spot for a long time. Don’t wear clothing that restricts blood flow in your legs. Don’t smoke. Don’t participate in contact sports when taking blood thinners because you’re at risk of bleeding from trauma.
How long does vein thrombosis last?
Most patients with deep vein thrombosis or PE recover completely within several weeks to months without significant complications or long-term adverse effects. However, long-term problems can occur, with symptoms ranging from very mild to more severe